Injection molding at the center of our activity.
We have a technical department able to design the moulds, automation and assembly lines. To support the production, and therefore our customers, we provide a mechanical workshop to improve the efficiency and / or modify the tools available.Overview and features
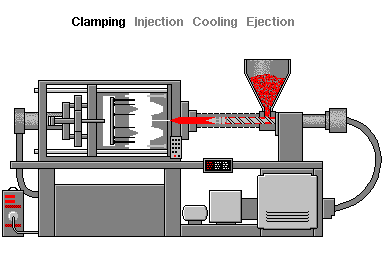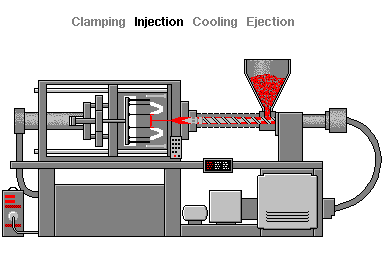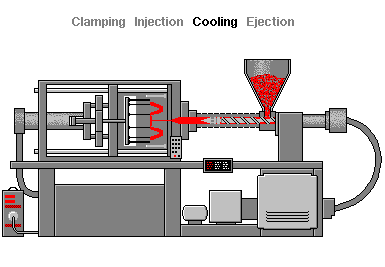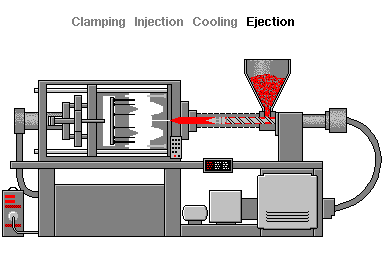
Injection molding is a forming process that uses molds. Materials such as synthetic resins (plastics) are heated and melted, then sent to the mold where they are cooled to take the designed shape. Materials are melted and poured into the mold (the Injection phase), where they harden (the Cooling phase). Once hardened, the products are extracted and finished (the Ejection phase).
With injection molding it is possible to produce in a continuous and rapid way and in large volumes pieces of different shapes, even complex ones. This is why injection molding is used to manufacture commodity products for many types of industries.
Injection molding process
How it works
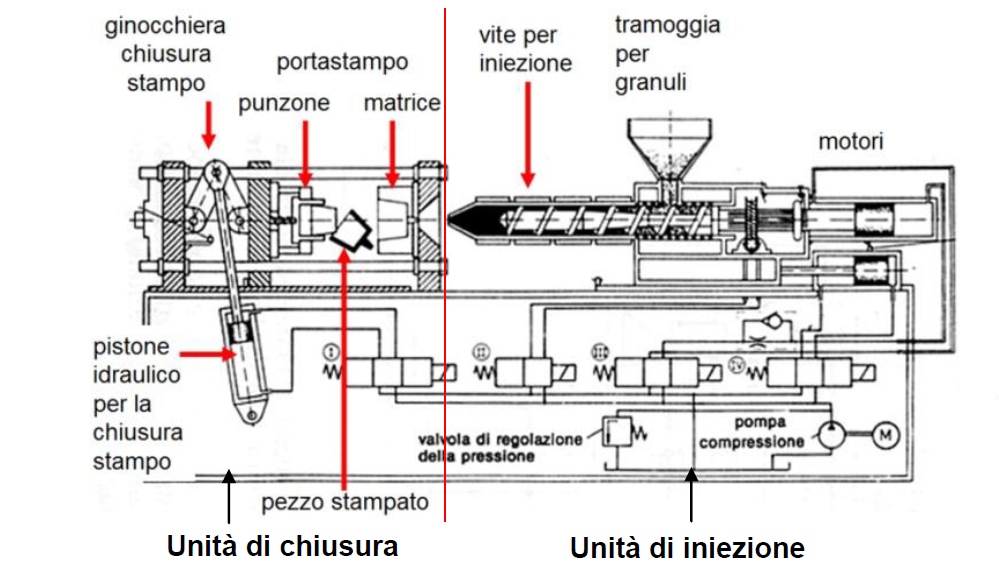
Injection molding begins with the pouring of resin pellets (granules) into the hopper, the material entry point. The pellets are then heated and melted inside the barrel in preparation for injection. The material is then forced through the nozzle of the injection unit before ending up in the mold called the sprue and then, through branched channels, into the mold cavity. After the material has cooled and hardened, the mold opens and the molded part is ejected from the mold. To finish the molded part, the sprue and sprue are cut away.
It is important that the molten material is evenly distributed throughout the mold, because there is often more than one cavity within the mold to allow for the production of more than one part at a time. Therefore, the shape of the mold should be designed to ensure this possibility, for example by having channels of the same size.
Although injection molding is suitable for mass production, it is essential to have a good understanding of the various conditions required to produce high-precision products, including resin material selection, mold processing precision, temperature and injection speed of the molten material.